Explain the Different Feeding Styles of Benthic Dwellers Including
Some benthic macroinvertebrates such as midges are small and grow no larger than 12 inch in length. Macroinvertebrates include aquatic insects such as mayflies stoneflies caddisflies midges beetles snails worms freshwater clams mussels and crayfish.

Benthic Pelagic Coupling An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Ram feeding and suction feeding.

. -Scavengers and deposit feeders. Many benthic creatures particularly clams and worms serve as food for larger economically important species such as blue crabs striped bass spot croaker and white perch. Benthic bottom-dwellers insects can cling sprawl climb and burrow.
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean lake or stream including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layersThe name comes from ancient Greek βένθος bénthos meaning the depths Organisms living in this zone are called benthos and include microorganisms eg bacteria and fungi as well as larger. Some benthic macroinvertebrates like midges are small and may grow no larger than one-half inch in length. Benthic taxa tend towards slightly more robust bodies and higher metabolic rates relative to gelatinous zooplankton.
Obtaining nutrients from particles suspended in water. Out of all marine species 98 of them can be found on the ocean floor making the benthic zone the lifeblood of diversity in the ocean comprised of mostly scavengers or detritivores organisms that feed off of dead organic material. Have evolved various behaviors for capturingsubduing prey.
Benthic meaning bottom-dwelling macroinvertebrates are small aquatic animals and the aquatic larval stages of insects. Others like the three ridge mussel can be more than ten inches long. The benthic zone is home to a massive amount of oceanic life referred to as benthos or bottom-dwellers.
They lack a backbone are visible without the aid of a microscope and are found in and around water bodies during some period of their lives. Others like the three-ridge mussel can be more than ten inches long. Obtaining nutrients by eating all of an organism.
Additionally the bacteria decomposers and detritus-feeders that live at the bottom of the Bay break down waste products and dead plants and animals. Obtaining nutrients by consuming other organisms fluids. Obtaining nutrients from particles suspended in soil.
Sponges appear to be the archetype filter feeders at the level of the organism Figures 1716 and 1717. In addition to being sensitive to changes in the streams overall ecological integrity benthic macroinvertebrates have other advantages as. While much of the food for these animals is stirred off the bottom by wave action currents or the activities of animals a good proportion is truly planktonic.
Japonicus feeding on 6 different types of diets with the ingredient of either pure powder of. Directly capture and eat other animals. There are many modes of feeding that animals exhibit including.
Many benthic organisms are planktivorous. Feed on food items that occur as deposits. The benthic invertebrates typically include sea stars sea anemones corals worms sea urchins sponges bivalves crabs and many more.
Clams mussels and crayfish. They include dragonfly and stonefly larvae snails worms and beetles. Some on large algae like kelps.
Metabolic variability in unsighted pelagic groups figure 3 b appears to reflect different feeding strategies ranging from float-and-wait predators to the more active tactile foraging found in some gymnosome molluscs. Including detritus and various detritus coated sediment. Usually locate prey using its chemical trail.
Using their radula most feed on fine algae. Feeding and Nutrition Gastropods -Exhibit wide variety of feeding style. The benthic zone includes submerged plants and animals like crabs prawns fishes and lobsters that will remain on the bottom of the marine layer.
Filter feeding organisms use specially designed structures to filter food from seawater. A 70-day experiment was conducted to examine the carbon isotopic signatures of A. The benthic invertebrates typically include sea stars sea anemones corals worms sea urchins sponges bivalves crabs and many more.
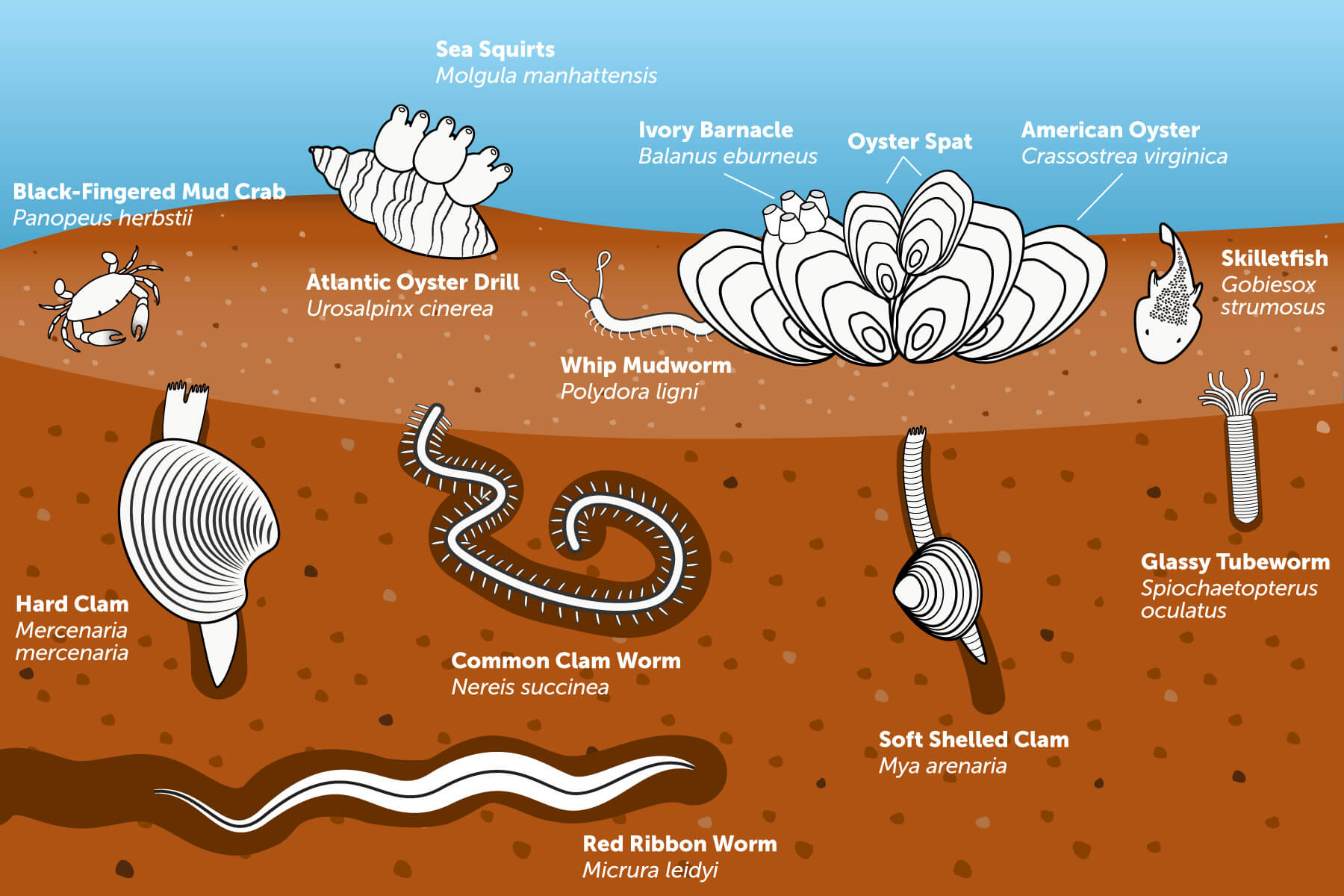
Life At The Bottom Chesapeake Bay Program

Three Types Of Animal Microbe Interactions That Interfere With Benthic Download Scientific Diagram

Schematic Drawing Of Different Feeding Behaviours Of European Download Scientific Diagram
Figure C 3 Feeding Types Of Benthic Organisms After Rhoads 1974 Download Scientific Diagram
0 Response to "Explain the Different Feeding Styles of Benthic Dwellers Including"
Post a Comment